

Localizer (LOC) and glide slope (G/S) carrier frequencies are paired so that the navigation radio automatically tunes the G/S frequency which corresponds to the selected LOC frequency. The cockpit instrument uses the difference between the modulation strengths of the two received signals to indicate left or right deviation from centerline.

The signals' phases at the antenna elements are arranged such that the 150 Hz signal is more prominent (has a greater depth of modulation) at a receiver located to the right of centerline, and the 90 Hz signal is more prominent to the left. In addition, a clearing signal is transmitted at one tenth of the power with a wider beam to prevent receivers from picking up the side lobes of the main beam.
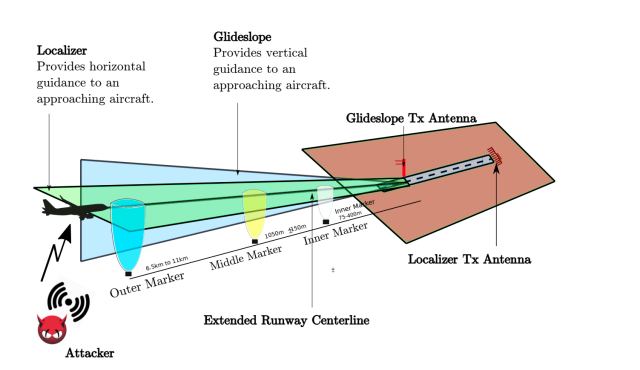
These are transmitted from co-located phased array antenna elements. One is amplitude modulated at 90 Hz, the other at 150 Hz. Two signals are transmitted on one of 40 ILS channels. Some runways have ILS only in one direction, this can however still be used for the opposite direction (with a lower precision) known as back beam or "Back Course" which is not associated with a glide slope. In parts of Africa and Asia large airports may lack any kind of transmitting ILS system. An older aircraft without an ILS receiver cannot take advantage of any ILS facilities at any runway, and much more importantly, the most modern aircraft have no use of their ILS instruments at runways which lack ILS facilities. In aviation, a localizer is the lateral component of the instrument landing system (ILS) for the runway centerline when combined with the vertical glide slope, not to be confused with a locator, although both are parts of aviation navigation systems.Ī localizer (like a glideslope) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. Emission patterns of the localizer and glide slope signalsĪn instrument landing system localizer, or simply localizer ( LOC, or LLZ prior to 2007), is a system of horizontal guidance in the instrument landing system, which is used to guide aircraft along the axis of the runway.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
